Polyvinyl butyral (PVB), due to its excellent transparency, toughness, superior metal adhesion, and good film-forming properties, occupies an important position in coatings, adhesives, printing inks, and safety glass interlayers. By adjusting the degree of polymerization (molecular weight), degree of acetalization, and residual hydroxyl content, PVB is endowed with diverse physicochemical properties, forming a matrix of specifications to meet different industrial needs.

1. Core Specification System: Performance Comparison of HX, SY, and TX Series
The differences in PVB specifications are mainly reflected in two dimensions: viscosity (molecular weight) and degree of acetalization.
1.1 Differences in Viscosity (Molecular Weight) Grades
Viscosity is a core indicator determining the processing fluidity and film strength of PVB.
♠ Low-viscosity grades (PVB Resin B-02HX, CCP B-03HX):
Performance characteristics: Excellent dissolution speed and low viscosity at high solid content, with strong permeability.
Key applications: Mainly used in printing inks, metal foil coatings, and penetrating primers. Due to its shorter molecular chains, it provides a smooth film surface and good wettability.
♠ Medium-viscosity grades (CCP B-06HX, Changchun PVB B-08HX):
Performance characteristics: Balances processability and toughness, making it the most widely used "all-rounder" grade.
Key applications: Widely used in wood coatings (sealers) and ceramic adhesives. Its viscosity is sufficient to maintain pigment suspension while ensuring the strength of the green body after sintering.
♠ High-viscosity grades (Changchun PVB B-17HX, PVB B-20HXB):
Performance characteristics: High molecular weight, resulting in extremely high impact strength and tensile strength after film formation.
Key applications: Primarily used in safety helmets/composite materials and peelable protective films. In these areas, PVB provides strong structural support, preventing materials from shattering under stress.
1.2 Trade-off between Degree of Acetalization and Polarity
♣ HX series (standard type): The degree of acetalization ranges from 72-88wt%, providing good general solubility (e.g., in alcohol solvents).
♣SY series (high degree of acetalization): This series has a higher butyral group content. Comparative Advantages: Increased acetal content means enhanced hydrophobicity. Compared to the HX series, the SY series exhibits superior solubility in non-polar solvents (such as methyl ethyl ketone and toluene mixtures), lower water absorption, and better dimensional stability. It is commonly used in special paints or precision electronic adhesives requiring excellent water resistance.
♣ TX Series (Special Modification):
Comparative Advantages: Designed for high-temperature processing environments. Its optimized residual hydroxyl group distribution significantly improves heat resistance after crosslinking with resins.
Key Applications: Specifically used in printed circuit boards (PCB) and copper foil adhesives, capable of withstanding the high temperatures during the soldering process.
2. Comparison of Solubility Behavior in Different Solvent Systems
The performance of PVB is highly dependent on the choice of solvent. The manual indicates that PVB is readily soluble in alcohols, ketones, and esters, but insoluble in pure hydrocarbons.
Solvent Strength Comparison: Alcohols (such as ethanol and isopropanol) are the most commonly used solvents, providing stable viscosity; while adding a small amount of aromatic solvents (such as toluene and xylene) not only reduces costs but also effectively lowers system viscosity and improves coating efficiency.
Effect of Water Content: PVB is extremely sensitive to water. The manual emphasizes that even a very small amount of water in the solvent can lead to a sharp increase in solution viscosity, or even gelation. Therefore, in safety glass or optical films requiring high transparency, the solvent specifications must be strictly controlled.
3. Comparison of PVB's Functional Roles in Multiple Fields
Adhesion vs. Sintering Residue (Ceramic Industry)
In ceramic adhesives, compared to other organic resins, PVB's advantage lies in its extremely high green strength. It allows the powder to be tightly packed in the mold and has a "residue-free" characteristic during the sintering process, ensuring the electrical performance and mechanical structure of the ceramic product.
Anti-corrosion Function vs. Decorative Function (Metal Coating)
In wash primers, PVB reacts with chromates and phosphates to form a chemically bonded layer on the metal surface, providing excellent anti-corrosion performance. This contrasts sharply with its role as purely a leveling agent and film-forming agent in baked enamel coatings for metal cans.
Enhanced Toughness (Resin Modification)
When PVB is used in combination with epoxy resin or phenolic resin, its function shifts from being the "main film-forming component" to a "modifier." Compared to the brittleness of pure epoxy resin, the addition of PVB significantly improves impact toughness and adhesion to metals due to the incorporation of long-chain PVB into the cross-linked network formed during the resin curing process.
Low-viscosity grades prioritize flow and penetration, making them ideal for inks and primers;
High-viscosity grades prioritize strength and toughness, making them core components for structural materials and protective films;
High acetal content and modified grades (SY/TX) provide specialized solutions for extreme environments requiring water and heat resistance.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
In the industrial application of chloroprene rubber, the processing performance and physical properties of the rubber vary significantly depending on the type of regulator used during the polymerization process. CR121 and CR322 are two highly representative general-purpose chloroprene rubbers. This article will analyze the specific differences between sulfur-modified (CR121) and mixed-modified (CR322) chloroprene rubber from three dimensions: technical characteristics, processing performance, and application selection, providing professional reference for production and processing.
1. Comparison of Technical Characteristics and Performance Indicators of CR121 and CR322
CR121 belongs to the classic sulfur-modified chloroprene polymer. This type of rubber uses sulfur as a regulator during polymerization, and its molecular chain contains a certain amount of sulfur segments, which gives it good tear resistance and flexural resistance. In terms of physical form, CR121 is a yellowish-white or light brown block, with a density of 1.23. From a performance standard perspective, the crystallization rate of CR121 is at a medium-to-low level, its tensile strength is not less than 24 MPa, and its elongation at break is excellent, usually above 900%. In industry standards, CR121 is similar to Dupont Neoprene GNA and Denka Chloroprene PM-40.
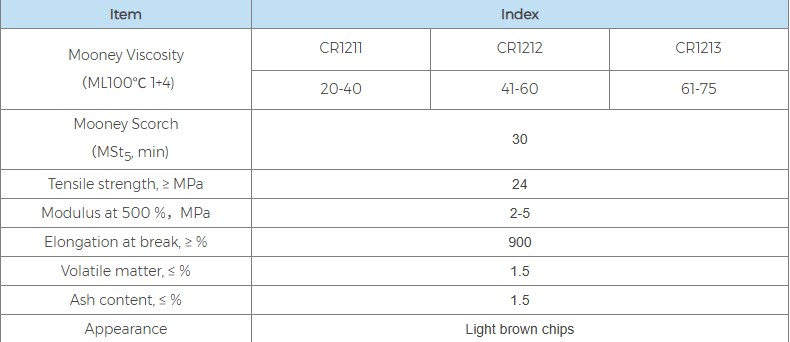
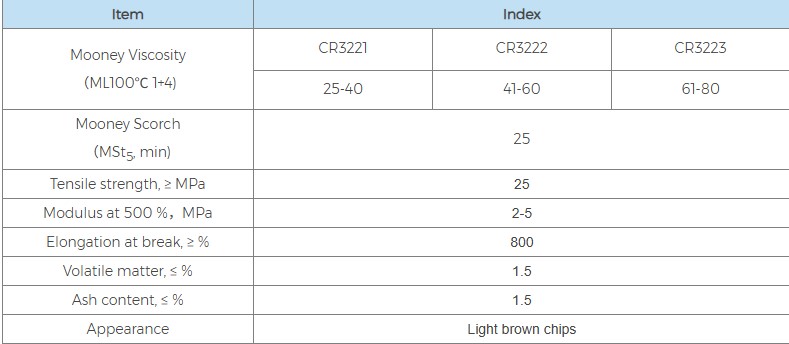
In contrast, CR322 is a chloroprene polymer that uses sulfur and diisopropyl xanthate disulfide as mixed regulators. This "mixed modification" mode aims to retain the advantages of sulfur-modified types while introducing xanthate to improve the stability and processing flexibility of the rubber compound. CR322 is also a yellowish-white or light brown block, with a density of 1.23, and its crystallization rate is also medium-to-low. In terms of core physical indicators, the tensile strength of CR322 is slightly higher than that of CR121, reaching over 26 MPa, but the elongation at break is slightly lower, approximately 800%. This model is similar in performance to Dupont Neoprene GW.
In terms of Mooney viscosity, both offer subdivided grades to meet different needs. CR121 includes specifications such as CR1211 (20-40), CR1212 (41-60), and CR1213 (61-75). CR322 correspondingly offers grades such as CR3221 (25-40), CR3222 (41-60), and CR3223 (61-80). Both exhibit consistent Mooney scorch time, requiring more than 30 minutes, ensuring good thermal stability.
2. Analysis of Differences in Processing Performance and Physical Strength
Although CR121 and CR322 are similar in some basic physical indicators, the actual production experience brought about by "mixed modification" and "pure sulfur modification" is quite different.
The core advantage of CR121 lies in its extremely high elastic reserve and excellent dynamic fatigue resistance. Due to its elongation at break reaching 900%, under working conditions requiring significant stretching or frequent bending, the molecular chains of CR121 exhibit stronger fatigue resistance. However, the disadvantage of the pure sulfur modified type is that it requires stricter processing techniques, especially during mixing and extrusion, where the control of rubber flow and viscosity requires extensive experience.
CR322 is designed to compensate for the shortcomings of traditional sulfur-modified types. Official technical data shows that CR322 has better processing performance than pure sulfur-modified rubber. In actual production, due to the introduction of xanthate modifiers, CR322 has better plasticizing performance and more stable molding fluidity. In addition, CR322's tear strength is particularly outstanding, which matches its tensile strength of 26 MPa. This means that in situations involving sharp objects scratching or strong tearing, CR322 can provide more robust structural protection than CR121.
Furthermore, in terms of storage stability, both are basically the same. From the date of manufacture, they can be stored for one year below 20℃ and for six months below 30℃. However, in extreme climates or complex warehouse environments, the mixed-modified CR322 often exhibits better resistance to physical property degradation than the pure sulfur type, thanks to its diversified molecular structure improvements.
3. Typical Application Scenarios and Selection Guidelines
The choice between CR121 and CR322 depends primarily on the dynamic load requirements and manufacturing process of the final product.
♠ Applicable Scenarios for CR121: Due to its excellent flexural resistance and high elongation, CR121 is the preferred choice for manufacturing high-performance transmission products.
Industrial belts: Including conveyor belts, multi-ribbed belts, V-belts, and synchronous belts. In these applications, the rubber is repeatedly bent around pulleys, and the excellent bending fatigue resistance of CR121 significantly extends the belt's service life.
Heavy-duty cable sheathing: Especially for mining cable sheathing and other applications requiring frequent movement and dragging, the tear resistance and flexibility of CR121 provide reliable physical protection.
♠ Applicable Scenarios for CR322: Thanks to its higher physical strength and optimized processing rheology, CR322 performs better in structural rubber components.
Hose products: CR322 is commonly used in the manufacture of various chemical-resistant and weather-resistant industrial hoses. Its high tear strength ensures that the hose body is less prone to structural failure under pressure or external abrasion.
Complex molded parts: Due to its superior processing performance compared to sulfur-modified types, for rubber parts with complex shapes and high mold cavity filling requirements, using CR322 can effectively reduce the scrap rate and improve production efficiency.
Specialty tapes: In the manufacture of tapes requiring extremely high strength, CR322, with its tensile strength advantage of 26 MPa, can provide stronger load-bearing capacity.
Summary: If you are pursuing ultimate flexibility and dynamic fatigue resistance (such as synchronous belts and V-belts), CR121 is the technical "gold standard." If your production process requires high fluidity and moldability of the rubber compound, or if your product requires higher tensile strength and tear protection (such as pressure hoses and high-strength seals), then the mixed-modified CR322 will be a more efficient and cost-effective choice.
In practical applications, users also need to make fine adjustments based on specific grades (such as different Mooney viscosity levels). For example, CR1211 is suitable for processes requiring good flowability, while CR3223 is suitable for heavy industrial applications that demand higher hardness and tensile strength. Understanding the chemical modification mechanisms of these two materials is crucial for improving the quality of rubber products.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
1. Mechanism of Elvanol in Paper Surface Treatment
In the modern paper industry, surface treatment has become an important means of increasing the added value of paper. Printability, surface strength, and barrier properties against oils and solvents all highly depend on the material selection of the surface sizing or coating system. Elvanol polyvinyl alcohol, as a high-performance water-based film-forming material, is widely used in paper surface treatment.

Elvanol is a fully or highly hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol with excellent film-forming ability. Its regular molecular chain structure allows it to form a continuous and dense film during drying, significantly improving the surface strength and barrier properties of the paper. Compared to using starch alone, the film formed by Elvanol is tougher, has stronger chemical resistance to oils, waxes, and solvents, and exhibits higher water resistance.
Using Elvanol in the sizing press or calendering stage can significantly improve the paper's resistance to linting, dusting, and cracking. Even at low addition levels (approximately 10% solids content), it can achieve surface strength and folding strength superior to traditional starch systems. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for high-filler paper, recycled fiber paper, and paper types requiring high printability.
In addition, Elvanol has good compatibility and can coexist stably with modified starch, CMC, alginates, wax emulsions, and common papermaking additives, providing greater flexibility for papermaking process adjustments.
2. Application Advantages of Elvanol in Improving Barrier, Strength, and Printing Performance
♣ Surface Barrier Properties
Elvanol is one of the most powerful water-based barrier film-forming materials in the paper industry. The film it forms has a natural barrier effect against oils, greases, and organic solvents, and is therefore often used in applications such as greaseproof paper, oil-resistant packaging paper, and copier paper. In oil-resistant systems, Elvanol can also serve as an effective carrier for fluorochemicals, improving the stability and efficiency of the overall barrier system.
♣ Surface Strength and Structural Stability
Compared to starch-sized paper, paper treated with Elvanol exhibits superior resistance to surface abrasion, cracking, and linting. Its high bonding strength effectively binds fibers and fine surface particles, reducing linting and dusting, thereby lowering the frequency of blanket contamination and downtime for cleaning during printing. This advantage is particularly evident in high-speed offset printing and high-precision printing.
At the same time, Elvanol allows for a higher proportion of fillers or recycled fibers while maintaining strength, helping paper mills control costs while maintaining paper performance.
♣ Printability and Coating Suitability
Elvanol-treated paper surfaces are smoother and have excellent ink holdout. Due to its oil and solvent resistance, ink does not easily penetrate the paper base, resulting in higher print gloss and image clarity. In pigment sizing systems, Elvanol, as a binder, exhibits significantly stronger binding power than acrylic emulsions, styrene-butadiene latex, casein, and starch, and can replace traditional binders at certain ratios, optimizing the pigment/binder ratio.
3. Typical Elvanol Grades and Application Characteristics in Papermaking
Based on different paper types and process requirements, we offer a variety of product grades with different viscosities and structures. The following are commonly used grades in the papermaking industry and their application characteristics:
| Grade | Polymer Type | Viscosity Level | Key Functions | Typical Uses |
| Elvanol 71-30 | Fully hydrolyzed PVOH | Medium | Film forming, binding, grease resistance | Surface sizing; FWA carrier; lint and dust control; grease-resistant papers |
| Elvanol 80-18 | Fully hydrolyzed PVOH | Medium | Grease barrier, high solids stability | Grease-proof packaging papers; high-solids sizing and coating |
| Elvanol 75-15 | Fully hydrolyzed PVOH | Medium–Low | Binder reinforcement | Starch reinforcement; lint reduction; high-solids sizing and coating |
In optical brightening systems, Elvanol acts as a carrier for fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs), significantly improving whitening efficiency. Adding Elvanol at 0.5–2.5% of the pigment weight in pigment systems results in significantly better whitening effects than using FWA alone, while also reducing the amount of traditional carriers such as starch and casein.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
In the modern field of fine chemicals, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), as a versatile water-soluble polymer, is widely used in various industries such as papermaking, textiles, adhesives, and packaging materials. Among the many PVA products, the ELVANOL series, with its unique production process and excellent physicochemical properties, has become a high-performance benchmark in industrial applications.
1. Core Technological Advantages and Physicochemical Characteristics of ELVANOL
The primary reason for ELVANOL's high market recognition lies in its unique particle morphology and molecular structure design. This special production process significantly improves efficiency in practical operations.
♠ Excellent Solubility and Energy-Saving Benefits
Traditional polyvinyl alcohol often requires high temperatures and long stirring times during the dissolution process, which not only increases energy consumption but also limits its application in some continuous production lines. A major technological breakthrough of ELVANOL is its ability to dissolve simultaneously in the continuous cooking process of starch. For the papermaking and textile industries, this means that PVA can be directly mixed and processed with starch, eliminating the need for separate dissolution tanks or complex pre-treatment processes.
From a physical perspective, this improved water solubility directly translates into reduced production costs. The significantly shortened dissolution time improves the turnover rate of production equipment and significantly reduces the thermal energy consumption during the heating process. For large manufacturing enterprises pursuing ultimate cost control, this characteristic of ELVANOL has extremely high economic value.
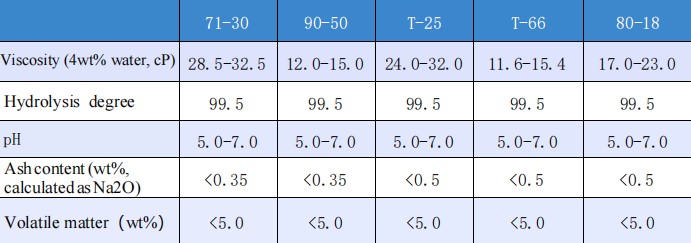
♠ Precise Viscosity and Degree of Hydrolysis Control
The ELVANOL series offers a variety of grades to meet different process requirements. For example, the Elvanol 71-30 grade has a viscosity range of 28.5-32.5 cP in a 4 wt% aqueous solution, while the Elvanol 90-50 grade is controlled at 12.0-15.0 cP. All mainstream grades (such as Elvanol 71-30 and Elvanol 80-18) have a degree of hydrolysis of 99.5%. This high degree of hydrolysis means that the molecular chain contains a very high proportion of hydroxyl groups, ensuring its excellent film-forming properties and extremely high adhesive strength. Meanwhile, its pH value remains stable between 5.0 and 7.0, exhibiting weak acidity to neutrality, and it possesses excellent chemical stability with most inorganic fillers and substrates.
♠ Synergistic Reinforcement Effect with Inorganic Materials
In compression molding or composite material manufacturing, ELVANOL demonstrates excellent mixing uniformity. It can form stable reinforced mixtures with fine powdered inorganic fillers. During the molding process, this uniformity prevents localized stress concentration, improving the structural integrity and surface finish of the final product.
2. Key Application Areas: From Paper Coating to Textile Warp Sizing
ELVANOL's application range covers multiple fields, from high-end adhesives to precision photosensitive coatings, with particularly outstanding performance in the paper and textile industries.
♣ Performance Multiplier in the Paper Industry
In paper coating applications, ELVANOL is typically used as a co-binder mixed with starch. Due to its excellent barrier properties, it effectively improves the paper's resistance to oil, grease, and oxygen. More importantly, ELVANOL's solubility in continuous cooking processes allows paper mills to simplify the coating preparation process. Through synergistic interaction with starch, it significantly enhances the surface strength of the paper, reducing dusting and linting during the printing process, making it particularly suitable for the production of high-end art paper and packaging cardboard. The T-Series Revolution in the Textile Industry: The Preferred Choice for Polyester/Cotton Blends
For the textile industry, ELVANOL has specially developed the T-series (such as Elvanol T-25) of unique copolymers. This series is designed specifically for polyester/cotton blends and other warp sizing applications.
A major challenge in textile processing is "desizing." Traditional sizing agents often require large amounts of chemical reagents during the desizing process, and the results are often unsatisfactory. The unique feature of the ELVANOL T-series is its stronger water solubility under alkaline conditions. In the finishing stage, the fabric only needs to be treated in a standard alkaline bath to achieve rapid and thorough desizing. This not only improves the dyeing uniformity of the fabric but also reduces chemical damage to the fibers. Diverse Industrial Applications
Besides its two main pillar industries, ELVANOL also plays an irreplaceable role in the following areas:
- Adhesives: With its high bonding strength and film-forming properties, it is used for bonding wood, paper, and porous materials.
- Ceramic Industry: As a green body binder, it improves the strength of molded green bodies.
- Photosensitive Coatings: Utilizing its high purity and low ash content (Na2O less than 0.35%-0.5%), it is used in precision electronic chemicals.
- Molding: Provides a more uniform molding effect, suitable for the manufacture of complex-shaped parts.
3. Environmental Attributes and Sustainable Development of Future Industries
Under today's stringent global environmental regulations and carbon neutrality goals, the environmental attributes of materials have become a core criterion for corporate procurement. ELVANOL was designed with environmental compatibility in mind from the outset.
♥ Biodegradable and Environmentally Harmless
ELVANOL is a polymer that poses no health hazards. In specific industrial wastewater treatment environments, it can be decomposed by microorganisms into carbon dioxide and water, greatly reducing the pressure on wastewater treatment systems. Compared to many synthetic plastic slurries, its biodegradability makes it a preferred material for green textiles and environmentally friendly packaging.
♥ Resource Recycling and Circular Economy
In the textile industry, the recycling of sizing agents is an important means of reducing costs and pollution. ELVANOL copolymers exhibit strong performance stability during recycling, and their film-forming and bonding properties do not significantly degrade even after multiple cycles. This makes it one of the most economical textile sizing agents on the market that meets environmental requirements.
♥ Indirect Environmental Benefits from Low Ash Content and High Purity
The volatile content of ELVANOL is consistently controlled below 5.0%. This high solid content and low impurity (low ash content) characteristic means that very few harmful gases and residual inorganic salts are released during the processing and heat treatment of the final product. This not only protects the precision of production equipment but also reduces the burden of exhaust gas treatment.
♥ Compliant with Sustainable Development Strategies
As consumer demand for sustainable products grows, companies using ELVANOL as a raw material can more easily obtain relevant environmental certifications. Whether in reducing production energy consumption or in the end-of-life treatment of products, ELVANOL demonstrates a forward-thinking industrial mindset: achieving a win-win situation between production efficiency and ecological balance through technological innovation.
The ELVANOL series of polyvinyl alcohol is not only a chemical raw material but also a mature industrial solution. Through special molecular design, it solves technical challenges such as dissolution efficiency, application strength, and alkaline desizing, while its biodegradable and recyclable properties address the contemporary demand for environmental protection.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
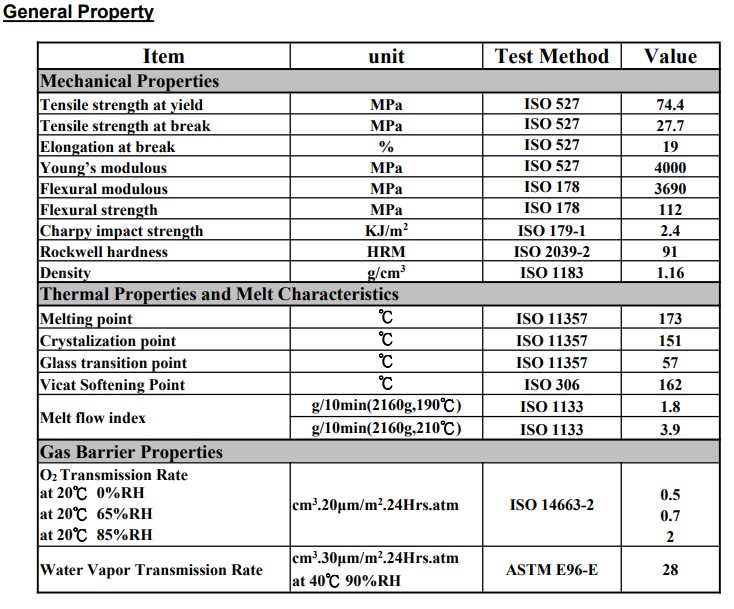
A Decision Guide Based on Performance Parameters: In the field of high-performance barrier packaging, Ethylene-Vinyl Alcohol Copolymer (EVOH) is a core material in multi-layer co-extrusion processes due to its excellent gas barrier properties. The EVASIN series, a leading EVOH brand in the market, offers various grades with ethylene content ranging from 29% to 44%. For packaging manufacturers, choosing the right grade is not only crucial for the shelf life of the final product but also directly impacts processing stability and overall costs.
1. The Deep Connection Between Ethylene Content and Gas Barrier Performance
Ethylene content is the most fundamental indicator determining the physical properties of EVOH. EVASIN grades are usually named according to their ethylene content. Changes in ethylene content directly alter the crystallinity of the polymer, which in turn affects its oxygen permeability.
♣ Low Ethylene Content (EVASIN EV-2951F, 29% mol):
When the ethylene content is low, the hydrogen bonding between molecules is stronger, resulting in higher crystallinity. This gives it extremely high barrier properties in a dry state. The oxygen transmission rate of Evasin EV- 2951F is only 0.2 cm³·20µm / m²·24hrs·atm. For meat, high-end refrigerated foods, or chemicals that are extremely sensitive to oxygen and require a very long shelf life, the 29% content grade is the preferred choice. However, it should be noted that low-ethylene-content EVOH has a higher melting point (188℃), a narrower processing temperature range, and is relatively more sensitive to humidity.
♣ High Ethylene Content (Evasin EV-4451F, 44% mol):
As the ethylene content increases, the barrier performance decreases. The oxygen transmission rate of Evasin EV-4451F is 1.8, which is 9 times that of Evasin EV-2951F. However, high ethylene content provides better flexibility, a wider processing window, and superior humidity resistance. In storage environments with high humidity (above 65% RH), the barrier performance of high-ethylene-content grades decreases less significantly.
♣ Selection Logic:
If your product needs to be stored at room temperature for more than 12 months, you should prioritize models with a 29% - 32% content; if your production line requires high processing flexibility, or the product requires moderate barrier properties (such as films for daily chemical products), then models with 38% - 44% content offer better cost-effectiveness and ease of processing.
2. Melt Index and Mechanical Compatibility with Processing Technology
When selecting a model, in addition to the final performance, the compatibility of the material with existing extrusion equipment and compounding processes must also be considered. The melt index is a core parameter for measuring resin fluidity, directly determining the extrusion pressure, shear heat, and film uniformity.
♣ Applications of Low Melt Index Models (MI 1.7 - 1.9):
Evasin EV3251F (MI 1.7) and Evasin EV3851VS(Evasin EV3851FS) (MI 1.8) are typical low melt index specifications. These materials have high viscosity and melt strength in the molten state, making them ideal for blown film processes. In the blown film process, high melt strength ensures the stability of the film bubble, preventing rupture or uneven thickness under high-speed traction. In addition, low melt index materials also help to form a more stable melt curtain in the cast film process.
♣ High Melt Index and Special Process Models (MI 4.01 - 4.3):
Under 210℃ testing conditions, the MI of EV 3251F reaches 4.01, while EV 3251FT reaches 4.3. The higher fluidity makes it more suitable for high-shear cast film processes or co-extrusion. For complex multi-layer structures (such as 7-layer or 9-layer films), high-fluidity EVOH can better match the adjacent adhesive layers and support layers (such as PE or PP), reducing dead spots and crystal formation in the flow channel.
♣ Consideration of Melting Point:
The melting point difference between different models can be as high as 23℃ (165℃ vs 188℃). When selecting a model, you must confirm the heating system and die temperature control accuracy of your extruder. If choosing EV 2951F, the processing temperature usually needs to be set between 210℃ and 230℃. Improper temperature control can easily lead to material degradation and carbonization.
3. Targeted Model Recommendations for End-Use Packaging Scenarios
♣ Meat and Dairy Vacuum Packaging:
This application requires extremely high oxygen barrier properties, typically using a PA/EVOH/PE structure. EV 2951F is the benchmark in this field, maximizing the inhibition of aerobic bacteria growth. If deep drawing is involved, EV 3251FT is recommended. The "T" designation usually indicates optimization for thermoforming processes, providing better uniform stretching distribution and preventing thinning and embrittlement of the barrier layer at the container corners.
♣ MAP and Lidding Films:
For MAP packaging of fresh fruits and vegetables, a certain gas exchange balance is required. EV 3851F/V provides moderate barrier properties, preventing large amounts of external oxygen from entering while also assisting in gas regulation within the overall structure.
♣ Pesticide and Chemical Anti-Permeation Bottles:
In these applications, the focus is on blocking organic solvents and odors. Evasin EV4451F is often used in blow molding to produce multi-layer plastic bottles due to its good chemical resistance and processing stability. Although its oxygen barrier properties are slightly inferior, it performs excellently in blocking hydrocarbon permeation, and its stability under high humidity ensures the safety of chemical products in warehouse storage environments.
♣ Pipes and Underfloor Heating Systems:
In non-packaging applications, such as the oxygen barrier layer in underfloor heating pipes, long-term heat stability and flexibility are usually required. EV 4451V, with its lower melting point and higher ethylene content, exhibits excellent compatibility in simultaneous processing with polyolefin pipes.
♠ During B2B procurement and production preparation, it is recommended to follow the following process for initial model selection:
- Clarify barrier requirements: Based on O2 sensitivity. Choose 29% for extremely high barrier, 32%-38% for general barrier, and 44% for high moisture resistance/flexibility requirements. Matching processing technology: For blown film extrusion, prioritize low MI grades (1.7-1.9); for cast film or complex co-extrusion, select high MI grades (4.0 or higher).
- Confirm equipment temperature control: Ensure the extruder can stably provide the required melting temperature for the specific grade (especially for grades with 29% content).
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
1. Application Background of VAE in Panel Lamination
In furniture manufacturing, interior decoration, and functional panel processing, panel lamination is widely used to enhance surface aesthetics and performance. Common lamination materials include PVC film, decorative paper, wood veneer, and high-pressure decorative laminates (HPL). Different lamination materials place varying demands on adhesives in terms of initial tack, wet bond strength, heat resistance, and processing adaptability.
VAE (vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer) emulsions, due to their molecular structure combining polarity and flexibility, exhibit excellent overall performance in the field of panel lamination. In wet lamination processes, VAE can form a stable adhesive interface between porous substrates and non-porous lamination materials, making it particularly suitable for the lamination of PVC film with substrates such as medium-density fiberboard (MDF) and particleboard.
From a processing perspective, VAE systems have high equipment compatibility and can be used with various application methods such as roller coating and knife coating. They also cure in a relatively short time, meeting the efficiency and stability requirements of continuous production lines. Therefore, VAE has become a mature water-based adhesive system for surface decoration lamination of panels.

2. Key Advantages of VINNAPAS VAE in Lamination Performance
In panel lamination applications, the VINNAPAS VAE product series demonstrates several targeted advantages. First, in terms of adhesion to PVC film, these VAE emulsions typically exhibit high initial adhesion, quickly forming an effective bond under wet conditions, reducing process risks such as warping and slippage. This characteristic is particularly important for high-speed lamination lines.
| Products | Technical data | Film-to-Wood lamination | |||||
| Solids content | Viscosity, dynamic | Glass transition temperature | Adhesion | Heat Resistance | Setting Behavior | Water Resistance | |
| VINNAPAS 920 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 800 - 2000 mPa·s | approx. -20 °C | Excellent | Medium | Medium | High |
| VINNAPAS EAF 68 | 58.0 - 61.0 % | 4500 - 9500 mPa·s | approx. -35 °C | High | Medium | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 3588 | 62.5 - 64.0 % | 200 - 800 mPa·s | 2 - 8 °C | High | Medium | High | High |
| VINNAPAS EP 6300 | 62.0 - 64.0 % | 600 - 1500 mPa·s | approx. 0 °C | Excellent | Medium | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 6420 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 3500 - 5500 mPa·s | approx. 2 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 645 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 4000 - 9000 mPa·s | approx. 5 °C | High | Excellent | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 656 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 4000 - 9000 mPa·s | approx. 5 °C | - | - | - | - |
| VINNAPAS EP 7000 | 69.5 - 71.5 % | 1200 - 2700 mPa·s | approx. -3 °C | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | High |
| VINNAPAS EP 701K | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 2000 - 4000 mPa·s | approx. -10 °C | Excellent | Medium | High | High |
| VINNAPAS EP 706 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 3500 - 4500 mPa·s | approx. 0 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 709 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 2700 - 3700 mPa·s | approx. 7 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 710 | > 54.5 % | 4400 - 5400 mPa·s | approx. 0-4 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 724 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 1500 - 2500 mPa·s | approx. 19 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 745 | 54.0 - 56.0 % | 4000 - 9000 mPa·s | approx. 5 °C | - | - | - | - |
| VINNAPAS EP 756 | 54.5 - 56.5 % | 600 - 2000 mPa·s | approx. 0-4 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
| VINNAPAS EP 760 | 59.5 - 61.5 % | 2000 - 3000 mPa·s | approx. 0 °C | High | High | High | Medium |
Secondly, heat resistance and durability are crucial performance indicators for laminated panels in actual use. Through reasonable glass transition temperature (Tg) design, VAE emulsions maintain flexibility while ensuring heat resistance, preventing delamination or adhesive failure of laminated panels within a certain temperature range. This is of practical significance for products such as furniture and cabinets used in complex environments.
In terms of substrate adaptability, VINNAPAS VAE exhibits good wetting and penetration capabilities on a variety of polar substrates. Whether applied to MDF, particleboard, or paper and wood veneer surfaces, it forms a stable adhesive film structure, contributing to improved overall strength and appearance consistency after lamination.
Furthermore, fast curing speed is another important characteristic of this type of VAE product. The reasonable film-forming temperature and viscosity range allow it to quickly develop cohesive strength after pressing, shortening subsequent processing or stacking waiting times and increasing production speed. This advantage is particularly prominent in large-scale panel processing scenarios.
3. Typical Panel Lamination Applications and Selection Considerations
At the application level, VINNAPAS VAE is widely used in various panel lamination structures. For example, in the lamination of PVC film and wood substrates, VAE provides reliable bonding strength while maintaining a flexible feel, suitable for products such as cabinet doors and furniture side panels.
In the wet lamination of decorative paper and wood-based panels, the VAE system helps the paper to be fully wetted and adhere to the substrate surface, reducing bubbles and wrinkles and improving the stability of the decorative effect. These applications typically focus more on the rheological properties and open time of the adhesive to ensure a sufficient operating window.
For lamination structures with higher performance requirements, such as HPM, VAE emulsion can be an important component of the system, achieving good heat resistance and interlayer bonding strength through coordination with process parameters. When selecting, it is usually necessary to comprehensively evaluate technical indicators such as solid content, viscosity, and Tg.
In actual use, the VAE product should also be selected specifically based on factors such as production line conditions, pressing temperature and time, and substrate absorbency. By reasonably matching the adhesive performance with process conditions, it is possible to improve overall production efficiency and product consistency while ensuring lamination quality.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
In industrial applications, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) usually needs to be prepared as an aqueous solution to exert its properties. However, due to differences in PVA grades, degree of hydrolysis, and physical form, the dissolution process often encounters challenges such as clumping, foaming, or incomplete dissolution. This article will combine professional technical experience to detail the dissolution principles, operating methods, and defoaming techniques of PVA.

1. Dissolution Principles
The dissolution of PVA is a process of swelling followed by dissolution, and its efficiency is profoundly affected by molecular structure and physical form:
- Factors determining solubility: The solubility of PVA is mainly determined by its degree of hydrolysis, degree of polymerization, and shape.
- Effect of degree of hydrolysis: As the degree of hydrolysis decreases, the dissolution temperature of PVA decreases, and its water solubility increases.
◊ Fully hydrolyzed type: Highly dependent on temperature; below a certain temperature, it will not dissolve or will only partially swell.
◊ Partially hydrolyzed type: Although easier to dissolve, excessively high temperatures can easily lead to foaming and clumping.
- Effect of morphology: Powdered PVA (20-100 mesh) has a larger surface area, so its dissolution time is about half that of granular PVA.
2. Technical Issues in Preparing PVA Solutions
To prepare high-quality PVA solutions and avoid contamination, the following hardware and parameter settings must be considered:
2.1 Equipment Selection
A reaction vessel with a stirrer should be used. The material must be stainless steel, enamel, or iron lined with synthetic resin to prevent rust and chemical corrosion from contaminating the PVA solution.
2.2 Stirring Speed Control
The stirring speed needs to be precisely adjusted according to the PVA specifications and stirrer type:
- Double-winged spiral stirrer: 500-1000 rpm is recommended for fully hydrolyzed types; 100-300 rpm is recommended for partially hydrolyzed types.
- Frame stirrer: 80-150 rpm is recommended.
- Risk warning: Too low a speed can easily cause PVA to settle and clump; too high a speed can easily entrain air and produce a large amount of foam.
2.3 Heating Method
Direct steam injection heating (pressure 1-1.5 kg/cm²) is recommended, supplemented by jacketed steam heating to significantly shorten the time. Direct heating with an open flame is strictly prohibited to prevent scorching at the bottom of the container.
2.4 Suitable Temperature for Preparing PVA Solution
| PVA grade |
PVA 100-70 |
PVA 098-20 PVA 098-15 PVA 096-27 PVA 098-08 PVA 092-53 PVA 097-29 PVA 098-05 PVA 098-03 |
PVA 094-27 PVA 095-28 PVA 092-20 PVA 092-35 |
PVA 088-50 & PVA 2488 |
PVA 080-44 |
| Temperature(℃) | ≥95 | 90-97 | 75-90 | 65-85 | Room temperature to 50 °C |
3. Dissolution Procedure
Following a scientific sequence of adding materials and increasing temperature can effectively prevent clumping:
- Preparation Stage: Add a measured amount of room temperature water (approximately 30°C is recommended) to the dissolution tank.
- Material Addition and Dispersion: Start stirring (a slightly higher speed is recommended), and slowly add the PVA. The slower the addition, the better, to prevent clumping.
- Swelling Treatment: Stir and disperse thoroughly for about 30 minutes to allow the PVA to swell completely.
- Heating and Dissolution: Gradually increase the temperature to the appropriate temperature according to the table above, and maintain the temperature while stirring for 1-2 hours. For partially hydrolyzed types, the heating should be slow to prevent foaming and overflow.
- Product Inspection: After obtaining a completely transparent solution, filter out impurities before use.
4. Foaming Principle and Defoaming Methods
Foaming is the most common interfering factor in PVA dissolution, especially common in medium and partially hydrolyzed products.
4.1 Foaming Mechanism
- Air Release: PVA is a porous substance, and its pores contain air and volatile substances such as methanol and esters remaining from production.
- Structural Differences: Partially hydrolyzed PVA has larger spatial voids than fully hydrolyzed PVA. After absorbing water, it releases the air in the pores, forming foam.
- Surface Activity: Partially hydrolyzed aqueous solutions have higher surface activity, which reduces the gas-liquid interfacial tension, and the solution has a certain viscosity, increasing the mechanical strength of the liquid film, making it difficult for the foam to disappear.
4.2 Defoaming Methods
- Physical Immersion Method: Before dissolution, soak and swell the PVA in cold water to pre-release the air in the pores, and then gradually increase the temperature. This can effectively suppress foam generation.
- Intermittent Operation Method: When foaming occurs, immediately turn off the steam and pause or reduce the stirring speed. After the foam disappears, gradually increase the temperature and stirring speed. Repeating this 2-3 times can significantly reduce foaming.
- Chemical Defoaming Method: If necessary, 0.01-0.05% (by weight of the solution) of a defoaming agent can be added, such as n-octanol, tributyl phosphate, or polyether defoaming agents.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
- General Properties
Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin appears as white, spherical, porous granules or powder, with a specific gravity of 1.1; however, its bulk density is only 0.20~0.35 g/ml.
- Thermal Properties
The glass transition temperature (Tg) of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin ranges from 50°C for low degrees of polymerization to 90°C for high degrees of polymerization; the glass transition temperature (Tg) of polyvinyl acetal resin is between 90°C and 110°C; this glass transition temperature can also be adjusted by adding an appropriate amount of plasticizer to lower it to a suitable operating temperature.
- Mechanical Properties
Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin has excellent film-forming properties and imparts excellent tensile strength, tear strength, abrasion resistance, elasticity, flexibility, and gloss to coatings; it is especially used as an interlayer in laminated safety glass, giving the glass strong impact and penetration resistance, and remains irreplaceable by other materials to this day.
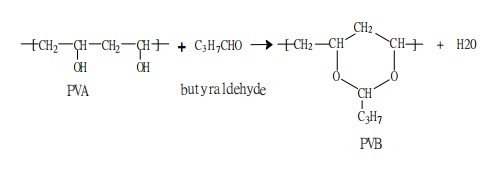
- Chemical Properties
Polyvinyl butyral (PVB) resin coatings have good water resistance, alkali resistance, and oil resistance (resistant to aliphatic, mineral, animal, and vegetable oils, but not castor oil). Because PVB contains a high hydroxyl content, it has good dispersibility for pigments, and is therefore widely used in printing inks and coatings. In addition, its chemical structure contains both hydrophobic acetal and acetate groups and hydrophilic hydroxyl groups, so PVB has good adhesion to glass, metals, plastics, leather, and wood.
- Chemical Reaction
Any chemical that reacts with secondary alcohols will also react with PVB. Therefore, in many PVB applications, it is often used in combination with thermosetting resins, allowing it to undergo cross-linking and hardening with the hydroxyl groups of PVB to achieve chemical resistance, solvent resistance, and water resistance. Of course, depending on the type of thermosetting resin and the mixing ratio with PVB, coatings with different properties (such as hardness, toughness, impact resistance, etc.) can be formulated.
- Safety Properties
Pure PVB is non-toxic and harmless to the human body. Because it can be used with ethyl acetate or alcohols as solvents, PVB is widely used in printing inks for food containers and plastic packaging.
As long as PVB does not come into direct contact with water, it can be stored for two years without significantly affecting its quality; PVB should be stored in a dry and cool place, avoiding direct sunlight, and heavy pressure should be avoided during storage.
- Solubility
PVB is soluble in alcohols, ketones, and esters. The solubility in various solvents varies depending on the functional group composition of the PVB itself. Generally, it is easily soluble in alcohol solvents, but methanol is less soluble for those with high acetal groups; the higher the acetal group content, the more easily it dissolves in ketone and ester solvents; PVB is easily soluble in alcohol ether solvents; PVB is only partially soluble in aromatic solvents such as xylene and toluene; PVB is insoluble in hydrocarbon solvents.
- Viscosity Characteristics of PVB Solutions
The viscosity of PVB solutions is greatly affected by the solvent formulation and the type of solvent. Generally, when using alcohols as solvents, the higher the molecular weight of the alcohol, the higher the viscosity of the PVB solution; aromatic solvents such as xylene and toluene, and hydrocarbon solvents can be used as diluents to reduce the viscosity of the PVB solution; the effect of PVB chemical composition on viscosity is summarized as follows: under the same solvent and the same content of each group, the higher the degree of polymerization, the higher the solution viscosity; under the same solvent and the same degree of polymerization, the higher the acetal or acetate group content, the lower the solution viscosity.
- PVB Dissolution Method
When using a single solvent or a mixed solvent, the dissolution process involves first adding the solvent, then adding the PVB at an appropriate speed while stirring. During the addition, avoid the formation of clumps of PVB (as this will increase the dissolution time several times), thus speeding up the dissolution process. Maintain appropriate stirring intensity to disperse and swell the PVB until it is completely dissolved, forming a completely transparent solution. Heating can also be used to shorten the dissolution time. Generally, a ratio of aromatic to alcoholic solvents of 60/40 to 40/60 (by weight) can produce a PVB solution with lower viscosity.
- Processing Properties
Although PVB resin is a thermoplastic plastic, it has almost no processability before the addition of plasticizers. Once plasticizers are added, its processability becomes very easy. PVB is compatible with plasticizers such as phosphate esters like TBP and TCP; phthalate esters such as DOP, DBP, and BBP; and castor oil, polyethylene glycol, and triethylene glycol di-butyrate. For general coatings and adhesives, plasticizers are added to modify the resin characteristics to meet application requirements, such as film flexibility, lowering the resin's Tg point, lowering the heat sealing temperature, and maintaining low-temperature flexibility.
- Compatibility
PVB is compatible with a variety of resins, such as phenolic resins, epoxy resins, alkyd resins, and melamine resins. CCP PVB B-08SY, CCP PVB B-06SY, and CCP PVB B-05SY, which have higher acetal content, can be mixed with nitrocellulose in any proportion. PVB and alkyd resins are partially compatible. General-purpose PVB is compatible with low-molecular-weight epoxy resins, while high-molecular-weight epoxy resins require the selection of PVB with high acetal content for compatibility.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L, a high-performance synthetic resin based on natural rosin and terpenes, modified with phenolic compounds, has become a mainstream choice in the global high-end adhesive market. Its excellent thermal stability and initial tack retention make it perform exceptionally well in industrial applications requiring extremely high bonding strength.
1. Technical Specifications and Physicochemical Properties Analysis of Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L
Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L was developed to fill the performance gap of general-purpose tackifying resins in extreme environments. From a technical perspective, 803L has stricter color control compared to the standard 803 model. The maximum Gardner color value is only 7, meaning it will not cause significant yellowing in light-colored or even transparent adhesive formulations.
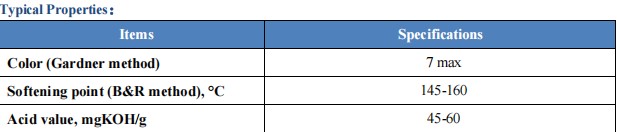
The product's softening point is stable between 145°C and 160°C. This high softening point characteristic gives the final adhesive product excellent heat resistance, especially maintaining the integrity of its physical structure at high temperatures without softening or sagging. In terms of acid value, the range of 45-60 mgKOH/g ensures good chemical affinity with various polar polymers.
From a molecular structure perspective, Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L has a very narrow molecular weight distribution. This characteristic is crucial in chemical production because it ensures consistent rheological properties of the adhesive during application. 803L fully meets the high standards of similar products from international brands in terms of polarity adjustment, solubility range, and improvement of initial tack. It not only significantly increases bonding strength but also extends the initial tack retention time of solvent-based adhesives, which is crucial for the positioning and application of complex workpieces.
2. Application Practices and Formulation Advantages in Different Industrial Fields
The versatility of Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L stems from its unique polarity balance, allowing it to be widely used in solvent-based adhesives, grafted CR (chloroprene rubber) adhesives, and hot-melt adhesives. Grafted CR Adhesive and High-Performance Shoe Sole Adhesives: In the footwear industry, particularly for bonding the soles of high-end leather shoes or athletic shoes, adhesives must possess extremely strong adhesion and aging resistance. 803L is commonly used in grafted chloroprene rubber (Grafted CR) adhesives. Due to its excellent compatibility, it forms a stable cross-linked system with chloroprene rubber polymers, and can effectively penetrate the substrate surface, especially when dealing with difficult-to-bond PVC artificial leather or genuine leather materials.
Hot Melt Adhesives and Tape Manufacturing: Although 803L has a high softening point, it exhibits broad compatibility with various elastomers (such as SIS, SBS, and EVA). When manufacturing high-performance hot-melt pressure-sensitive adhesives (HMPSA), the addition of Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L can significantly improve the peel strength and shear strength of the tape. For formulators looking for an alternative to YS POLYSTER T160 grade products, 803L provides thermal stability that effectively reduces carbonization caused by prolonged heating of the adhesive in the hot melt tank, extending equipment maintenance cycles.
Stability of High-Performance Solvent-Based Adhesives: In solvent-based formulations, 803L is soluble in many common solvents, such as toluene, ethyl acetate, or methyl ethyl ketone. It not only provides high initial tack but, more importantly, significantly improves the temperature resistance of the adhesive layer after drying. This makes it perform exceptionally well in applications sensitive to environmental temperature changes, such as automotive interior bonding and electronic component fixing, with performance comparable to TAMANOL 803L in similar applications.
3. Procurement Decisions in a Global Supply Chain: Quality Control and Logistics Advantages
The production process of Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L follows a strict quality management system, ensuring that the acid value, softening point, and color variations of each batch are within a very small range. For global buyers, this consistency means that frequent adjustments to formulation processes are not necessary when changing batches.
In terms of packaging, the product is typically packaged in standard 25kg composite paper bags. This packaging not only meets international transportation safety standards and effectively prevents moisture intrusion that can lead to resin clumping, but also facilitates forklift handling and warehouse stacking. During long-distance sea transportation, the resin maintains a stable physical form, ensuring that it remains uniformly granular and easy to handle upon arrival at the client's location.
As a highly cost-effective tackifying solution, Terpene Phenolic Resin 803L offers an excellent alternative for companies seeking high-performance terpene phenolic resins. Whether your existing formulation is based on TAMANOL 803L or YS POLYSTER T160, 803L, with its superior compatibility and physical properties, can help companies optimize their raw material cost structure and improve their bargaining power in the global supply chain without compromising the quality of the final product.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
In the field of paper packaging and post-processing, the performance stability of adhesives directly impacts production efficiency and product quality. With the increasing popularity of water-based systems in the packaging industry, VAE emulsions have gradually become the mainstream choice for cardboard boxes, paper cartons, and paper bags due to their excellent overall performance. The VINNAPAS series of VAE emulsions, through varying ethylene content and formulation designs, can cover a wide range of paper packaging applications.
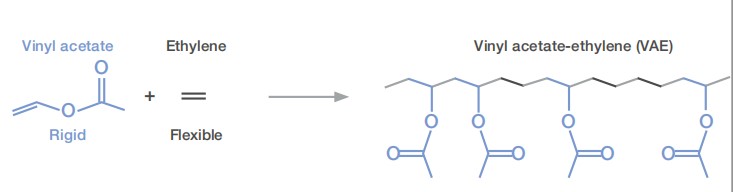
1. Technical Characteristics and Core Advantages of VINNAPAS VAE Emulsions
VINNAPAS VAE emulsion is a high-performance polymer dispersion whose molecular structure combines the advantages of vinyl acetate (providing cohesion and hardness) and ethylene monomers (providing flexibility and adhesion). This unique chemical structure gives it the following core technical advantages in paper packaging processing:
- Balanced performance: VAE emulsions achieve a good balance between adhesive strength, cohesion, and flexibility, ensuring stable bonding strength at different ambient temperatures.
- Excellent substrate adhesion: This series of products is not only suitable for traditional coated or uncoated paper and cardboard, but also has excellent wetting and adhesion to various "difficult-to-bond substrates" such as plastic films.
- Extremely fast curing speed: On high-speed automated production lines, curing speed directly affects productivity. WACKER VAE has a very high drying speed, which can meet the high-speed operation requirements of modern packaging equipment.
- Good wettability and low-temperature flexibility: Even in low-temperature environments, the VAE coating can maintain good flexibility, preventing the adhesive layer from becoming brittle, and has excellent penetration and spreading capabilities on the substrate surface.
2. Main Application Scenarios of WACKER VAE in Paper Packaging Processing
Paper box and carton sealing: This is the most common application area for VAE emulsions. Whether it's simple folding cartons or load-bearing cardboard boxes, VINNAPAS provides sufficient initial tack and final strength to ensure that the packaging does not delaminate during transportation.
Paper bags, document bags, and paper sacks: In paper bag manufacturing, bottom sealing and side bonding require adhesives with good workability and aging resistance. VAE emulsions (such as VINNAPAS EP 705 A) ensure the stability of seams in paper bags under load.
- Corrugated cardboard and paperboard: VAE emulsions are commonly used in the processing of high-performance corrugated cardboard, providing stronger bonding strength and moisture resistance than traditional starch adhesives.
- Lamination applications: In the lamination process of paper with plastic films (such as PE, PP, PET) or aluminum foil, VAE emulsions serve as the basis for high-performance adhesives, addressing the challenge of bonding non-polar surfaces.
- Folding carton processing: For high-end gift boxes, medicine boxes, and other folding cartons, VAE ensures that creases do not crack and exhibits excellent mechanical stability during the forming process.
3. Environmental Compliance and Food Safety Assurance
- Food contact safety: VINNAPAS VAE emulsions comply with the main relevant regulations for food contact materials and are suitable for manufacturing various food packaging adhesives.
- Low migration and no plasticizers: WACKER's technology allows for the formulation of adhesives without plasticizers, featuring low migration characteristics, significantly reducing the risk of packaging materials contaminating the food or pharmaceuticals inside.
- Sustainability: Some high-end models, such as VINNAPAS 920 and VINNAPAS EP 7000, do not use APEO (alkylphenol ethoxylates) in the production process and have extremely low formaldehyde content, fully complying with green and environmentally friendly production standards.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
- Bismaleimide Series2
- Cross-Linking agent / Vulcanizing Agent1
- Curing Agent1
- Engineering Plastic Pellets4
- Epoxy Resin2
- Ethylene-VinylAlcohol Copolymer(EVOH)1
- Fish Oil1
- Food Additives3
- Glucosamine1
- Heat-resistant modifier series1
- High Assay Quaternary Ammonium Compounds9
- Low Assay Quaternary Ammonium Compounds13
- Modified Polyvinyl Alcohol1
- Monomalemide Series2
- Other Surfactants/Catalysts8
- Plastic Random Packing1
- Plastic Structured Packing1
- Polyacrylamide1
- Polyurethane Resin2
- Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)2
- Power Coatings3
- Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxide4
- Special Quaternary Ammonium Compounds7
- TPU4
- Tertiary Amines1
- UV Ink1
- VAE Emulsion (Vinyl Acetate–ethylene Copolymer Emulsion)1
- aluminum paste1
- antiform2
- fire sleeve2
- resin2